You’ve hit Excel’s ceiling. VLOOKUP formulas stretching across columns. Macros that break mysteriously. Spreadsheets so large they crash when you open them. If this sounds familiar, you’re ready for Python — and the transition is easier than you think.
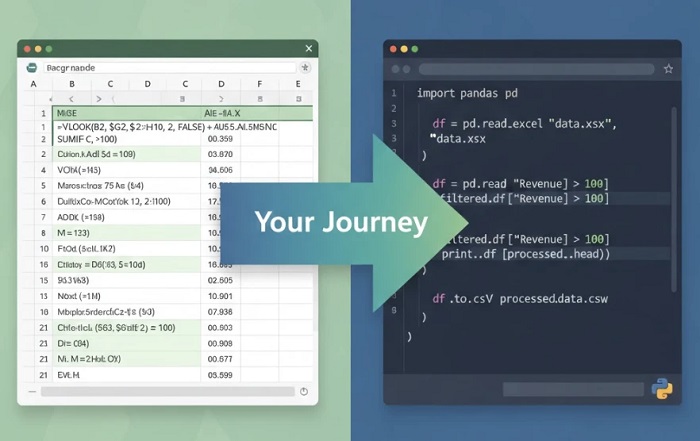
Python for data automation isn’t about abandoning Excel. It’s about gaining superpowers that extend what you can do with data. The same logic you use in spreadsheet formulas translates directly to Python code, but without the limitations. This guide maps your journey from Excel power user to Python automation specialist. For deeper coverage of these techniques, explore this complete guide to Python data automation.
Why Excel Users Excel at Python
Here’s a secret most programming tutorials won’t tell you: Excel experience is genuine programming experience. You’ve already developed the core skills Python requires.
You understand data structures. Rows and columns in Excel map directly to Python’s DataFrames. The mental model you’ve built for organizing data transfers completely.
You think in formulas. Every Excel formula is a tiny program. IF statements, nested functions, references — these concepts have direct Python equivalents. You’re not learning to think like a programmer; you’re learning new syntax for thoughts you already have.
You debug naturally. Tracing why a formula returns #REF! error? That’s debugging. Breaking complex calculations into steps to find problems? That’s the same process Python developers use daily.
You automate instinctively. Anyone who’s recorded a macro or created a template to avoid repetitive work already thinks like an automation developer. Python just removes the limitations.
What Python Adds to Your Toolkit
Understanding the specific gains helps motivate the learning investment:
Scale without limits. Excel struggles with 100,000 rows. Python handles millions without breaking a sweat. Your analysis isn’t constrained by spreadsheet limitations anymore.
True automation. Python scripts run unattended. Schedule them to execute at 6 AM, process overnight data, and have reports ready when you arrive. No clicking through prompts or babysitting processes.
Connect anything. APIs, databases, web services, cloud storage — Python connects them all. Pull data from Salesforce, process it, push to Google Sheets, email the summary. One script, fully automated.
Reproducibility. A Python script documents exactly what you did. No more “I think I filtered this column and then… maybe sorted?” Every step is written, version-controlled, and repeatable.
Professional growth. Excel skills plateau quickly in the job market. Python opens doors to data analyst, automation engineer, and data scientist roles with significantly higher salaries.
The Learning Path: Week by Week
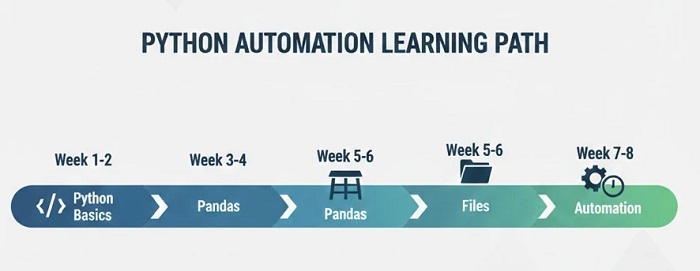
A structured timeline helps you progress without feeling overwhelmed:
Weeks 1-2: Python Fundamentals
Focus on core syntax that maps to Excel concepts:
- Variables → Named cells/ranges
- Lists → Rows or columns of data
- Dictionaries → Lookup tables
- Loops → Dragging formulas down columns
- Functions → Custom Excel functions
- Conditionals → IF statements
Don’t rush this phase. Spend time writing small scripts until syntax feels natural. Practice converting simple Excel formulas to Python code mentally.
Weeks 3-4: Pandas Introduction
Pandas is Python’s answer to spreadsheets. Everything you do in Excel has a pandas equivalent:
- Reading files:
pd.read_excel()— opens your spreadsheets directly - Filtering:
df[df['column'] > 100]— like Excel filters but in code - Formulas:
df['new_col'] = df['A'] + df['B']— column calculations - VLOOKUP:
pd.merge()— joins data from different sources - Pivot tables:
df.pivot_table()— exactly what you’d expect
Practice by recreating your most common Excel workflows in pandas. The familiarity accelerates learning dramatically.
Weeks 5-6: File Operations
Real automation requires working with files:
- Reading multiple Excel files from folders
- Writing results to new files
- Organizing and renaming files automatically
- Handling CSV, JSON, and other formats
- Dealing with encoding issues (the bane of data work)
Build a script that processes a folder of monthly reports into a single summary. This pattern appears constantly in real work.
Weeks 7-8: Automation Essentials
Transform scripts into hands-free automation:
- Error handling — scripts that don’t crash unexpectedly
- Logging — knowing what happened when you weren’t watching
- Scheduling — running scripts automatically at set times
- Email notifications — getting alerts when automation completes or fails
Your First Automation Project
Theory only goes so far. Here’s a practical first project that combines multiple skills:
The Monthly Report Consolidator
Scenario: You receive sales reports from five regional offices every month. Currently, you manually open each file, copy data, paste into a master sheet, update formulas, and create a summary. It takes two hours.
Python solution:
- Script scans a folder for this month’s regional files
- Reads each Excel file into pandas
- Combines all data into single DataFrame
- Calculates totals, averages, and comparisons
- Generates summary report with charts
- Emails report to distribution list
- Archives processed files to dated folder
Total runtime: 30 seconds. Your two-hour task becomes a scheduled script you never think about. This is the power of Python data automation.
Choosing Your Python Automation Training
With thousands of Python courses available, focus on these criteria:
Excel-to-Python bridge: The best training for spreadsheet users explicitly connects Python concepts to Excel equivalents. This accelerates comprehension dramatically.
Data focus over general programming: General Python courses teach web development, games, and everything else. For data automation, you need focused content on pandas, file operations, and practical data workflows.
Project-based learning: Watching tutorials creates illusion of progress. Courses requiring you to build actual automation projects teach skills that stick.
Real-world messiness: Clean tutorial data doesn’t prepare you for reality. Good training shows how to handle missing values, inconsistent formats, and the chaos of actual business data.
Ongoing support: Questions arise when applying skills to your specific situation. Training with community access or instructor support helps you push through obstacles.
Common Transition Challenges
Excel users face specific hurdles when learning Python:
- Missing visual feedback: Python requires running code to see results. Use Jupyter notebooks for interactive feedback while learning.
- Zero-indexed thinking: Excel starts at 1, Python at 0. You’ll adapt within days of practice.
- Error messages: Python tracebacks look overwhelming. Read just the last line first — it tells you what went wrong.
- Imposter syndrome: Remember you’ve been programming in Excel for years. Python is just a more powerful tool.
Measuring Your Progress
How do you know when you’re ready? Key milestones:
- You can read, transform, and write Excel files without constant syntax lookups
- You’ve automated something from actual work that saves real time
- When facing data tasks, you instinctively think “this would be faster in Python”
- Your scripts run scheduled and unsupervised — you trust them
- Colleagues start asking you to automate their workflows
The Career Impact
Python data automation skills change your trajectory. Excel power users earn $45,000-$65,000 typically. Add Python automation and the range jumps to $65,000-$95,000. Senior roles reach $110,000+. Beyond salary, you unlock new positions: Data Analyst, BI Analyst, Automation Specialist — roles that weren’t accessible with Excel alone.
Start Your Transition Today
The gap between Excel and Python is smaller than it appears. You already think about data correctly. You just need the syntax to express what you already know. Every week you wait is another week of manual work that could be automated.
Ready to transform your data work? The Python Automation Course is designed specifically for this transition — building on spreadsheet logic to teach practical automation skills you can apply immediately.











Leave a Reply